|
1. Regional
Geology
The
southwestern foothills belt is a fold-thrust fault comprised by several
imbricate thrust faults. The thrust faults starting from east to west
are the Tachienshan Fault, Chiuchiungkeng fault, and the Chiayi fault.
The Chiuchiungkeng fault stretches between the Kukeng fault and the
Chuchi fault. The hanging wall of the fault is the mudstone and
laminated sand-shale of the Cholan Formations; the foot wall is mainly
consisted of the thick layer sandstone Liushuang Formation. It was
discovered in the field that the Cholan Formation mudstone thrusts above
the late Pleistocene-Holocene conglomerate layer.
The
landforms of the two sides of the Chiuchiungkeng fault are highly
different: the hanging wall is a steeper foothill which slope is between
15-35º. The foot wall has an upheaval–a tableland of a slope under 10º.
Judging from the river pattern, the rivers in the coastal plain are
meandering rivers; the rivers in the upheaved tableland and hills (the
hanging wall of the Chiuchiungkeng fault) belongs to the incised
meanders and braided rivers. The analysis of the slope of the riverbed
also shows that there are significant slope differences between the two
sides of the fault. The river slope is 140 meter per kilometer in the
hanging wall; the river slope of the foot wall is less than 10 meters
per kilometer. It shows that the evident differences between the two
sides are resulted from the continual upheaval of the hanging wall of
the Chiuchiungkeng fault.
2.
Fault Character
The
Kukeng trench is situated in the linear scarp on the front edge of the
foothills, and the trenching strike is vertical to the linear scarp. (Figure
1, 2) A small terrace is located on the east of the linear scarp.
The trench is trenching in the form to two steps, 17 meters in length, 8
meters in width, and 4 meters in depth. (Figure
3,4) From the sediment formation revel on the trench profile, it
shows that the sediment environment belongs to the alluvial fan of the
front edge of the foothills. The sediment is thick gravel bed and
occasionally has some thin lenticular sand beds. The trench profile
shows no signs of the fault disturbed. Thus we conjectured that the
fault still be located to the east of the trench.
This
research has two core-boring in the Kukeng site. The lithologic
characters of the cores are both thick gravel bed, with a gray sand-mud
bed. The results indicate that there are no offsets within the gray
sand-mud bed. (Figure 5) The mudstone
bed of the Cholan formation has outcropped in the eastern 25 meters of
the Kukeng borehole 2. The Kukeng borehole 2 is 30 meters in depth, and
has yet not bored to the bedrock. We perceived that the fault should be
located to the east of the Kukeng borehole 2. (Figure 5)
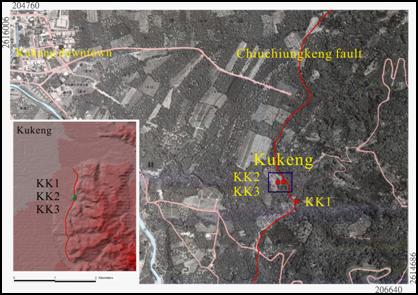
Figure 1,
The Kukeng site is located on the intersection of the hills and the
plains on the east
to Kukeng. (TWD 67)

Figure 2,
The Kukeng trench are mainly consisted of conglomerate sediments.
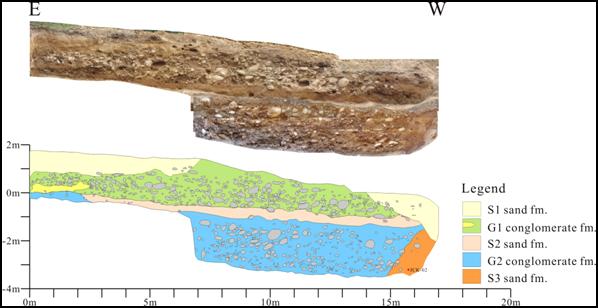
Figure 3,
The profile of the south wall.
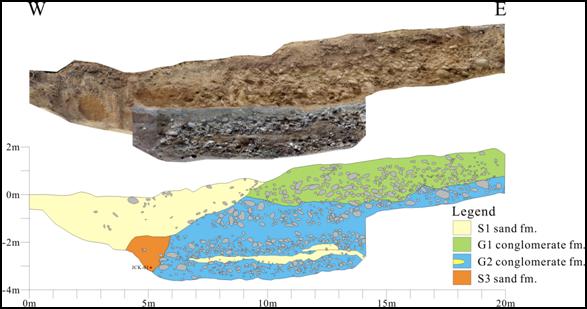
Figure 4,
The profile of the north wall.
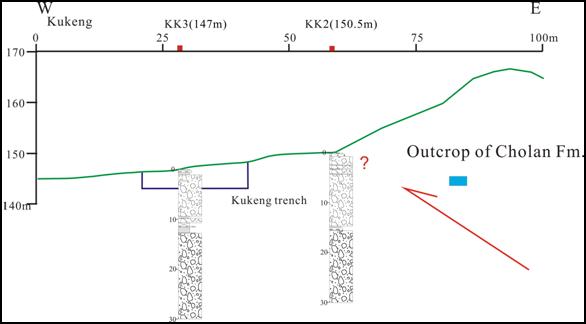
Figure 5,
The profile of the Kukeng site core-boring.
|